Python E-Commerce Demo#
In this example you will learn how to model your e-commerce website as a
directional graph, how to use actions, guards and shared state
in your graph model. You will learn how to use AltWalker’s online,
offline, walk, check and verify commands.
The tests are written in python with Selenium and PyPOM (Python Page Object Model). You can find the tests source code here.
The e-commerce website being tested is written in markdown and uses Jekyll to generate static files. For cart and order management it uses Snipcart. The website is hosted on GitHub Pages and its forked from Snipcart on GitHub.
Page Object Pattern#
Page Object is a Design Pattern which has become popular in test automation for enhancing test maintenance and reducing code duplication. A page object is an object-oriented class that serves as an interface to a page of your AUT. […] The benefit is that if the UI changes for the page, the tests themselves don’t need to change, only the code within the page object needs to change.
Model-Based Testing with Page Object Pattern#
When you are using Model-Based Testing with Page Object Pattern:
the Page Object Pattern separates your test code from the specific code that interacts with the AUT
the Model-Based Tests separates your test code from the flow of the AUT by abstracting the flow in the models.
Now if the UI changes you will only need to update the Page Objects and all the flows (from the model) will reflect the new changes. And if the flow changes you will only need to add new element to your model.
Setup#
For this Demo we used geckodriver to launch the Firefox browser.
Download geckodriver. After you download and extract the executable, make sure you set the path to the geckodriver executable in the
Pathvariable to make other programs aware of its location.
> set PATH=%PATH%;C:\bin\geckodriver
$ ln -s /path/to/geckodriver /urs/local/bin/geckodriver
Clone the examples repository:
$ git clone git@github.com:altwalker/altwalker-examples.git
$ git clone https://github.com/altwalker/altwalker-examples.git
Go into the e-commerce demo directory:
$ cd altwalker-examples/python-ecommerce
(Optional) Create a python virtual environment:
> python3 -m venv .virtualenv
> .virtualenv\Scripts\activate
$ python3 -m venv .virtualenv
$ source .virtualenv/bin/activate
Install the python dependencies:
$ pip install -r requirements.txt
Or:
$ python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt
Modeling#
We have modeled our e-commerce website as two graphs connected by two shared states. One of the models handles the navigation process of selecting a product and adding it to the cart and the other model handles the checkout process.
Each vertex in the graph represents a state (e.g. v_cart_not_empty). This
is where we put our asserts.
Each edge in the graph represents an action (e.g. e_add_to_cart,
e_go_to_product_page). This is where we put our page interaction code.
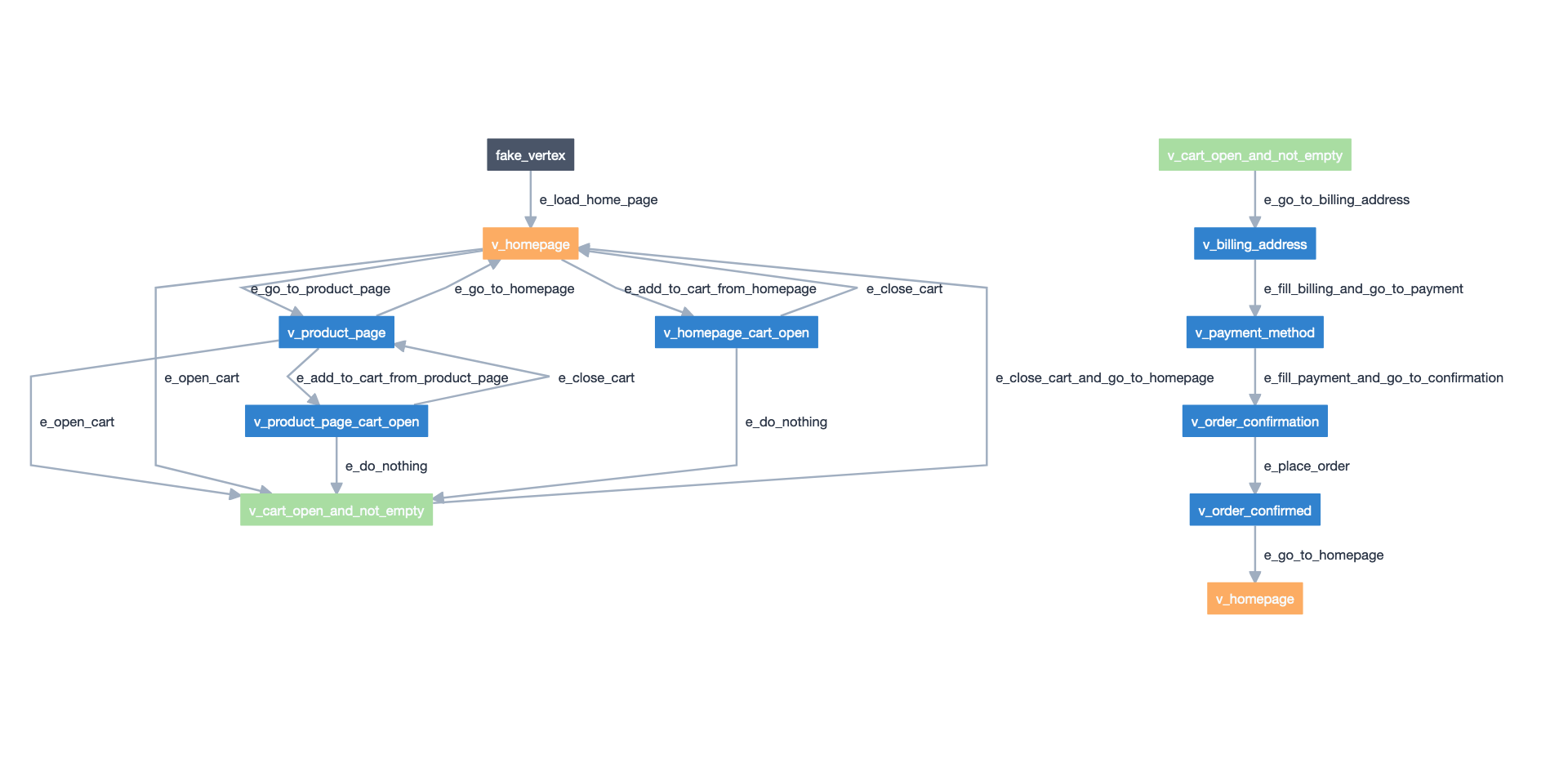
Screenshot of the models taken from the Model-Editor.#
The models/navigation.json contains NavigationModel and the
models/checkout.json CheckoutModel:
NavigationModel contains edges and vertices that verify homepage and product page behavior.
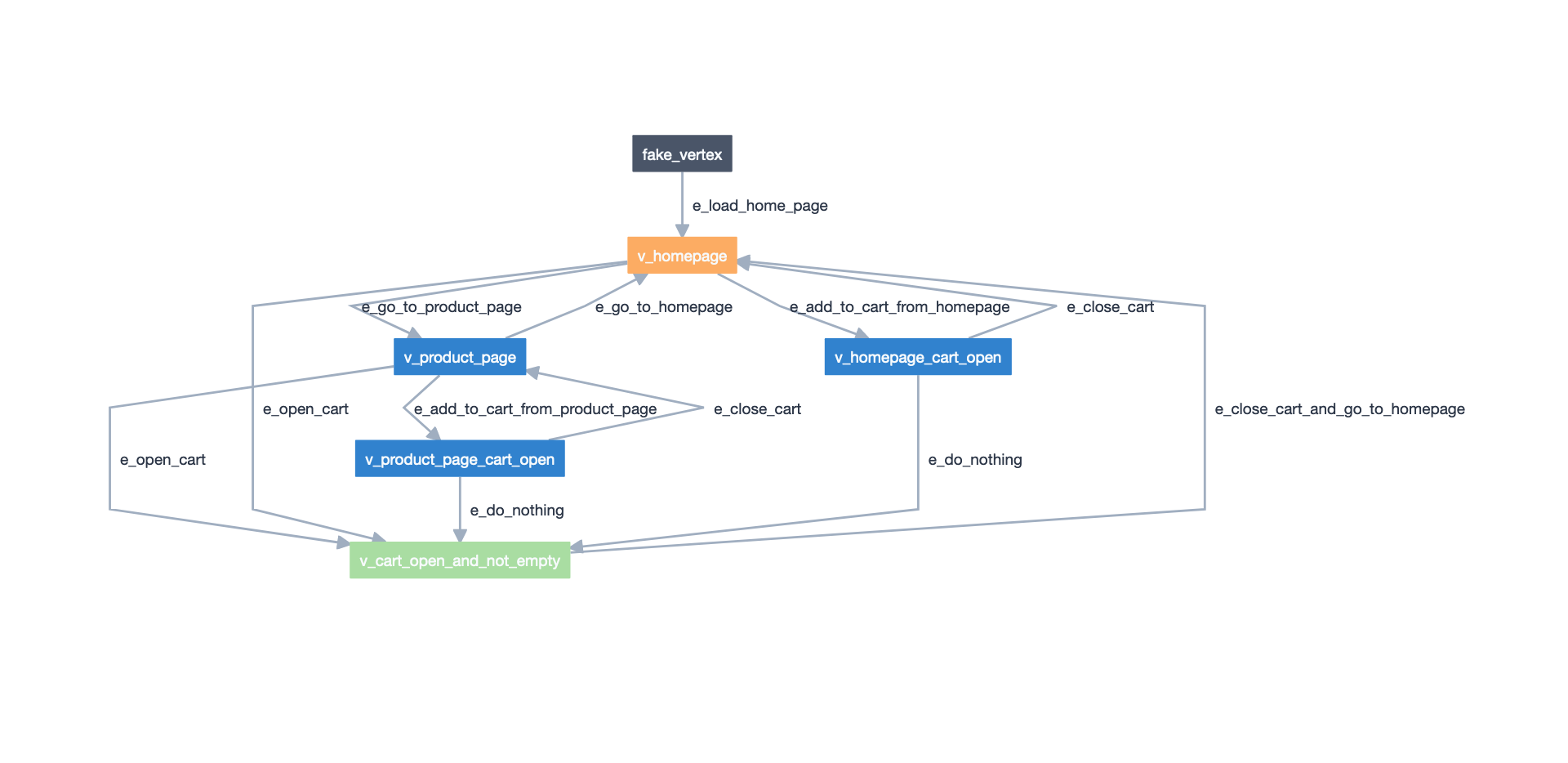
Screenshot of the NavigationModel taken from the Model-Editor.#
CheckoutModel contains edges and vertices that verify the checkout process.
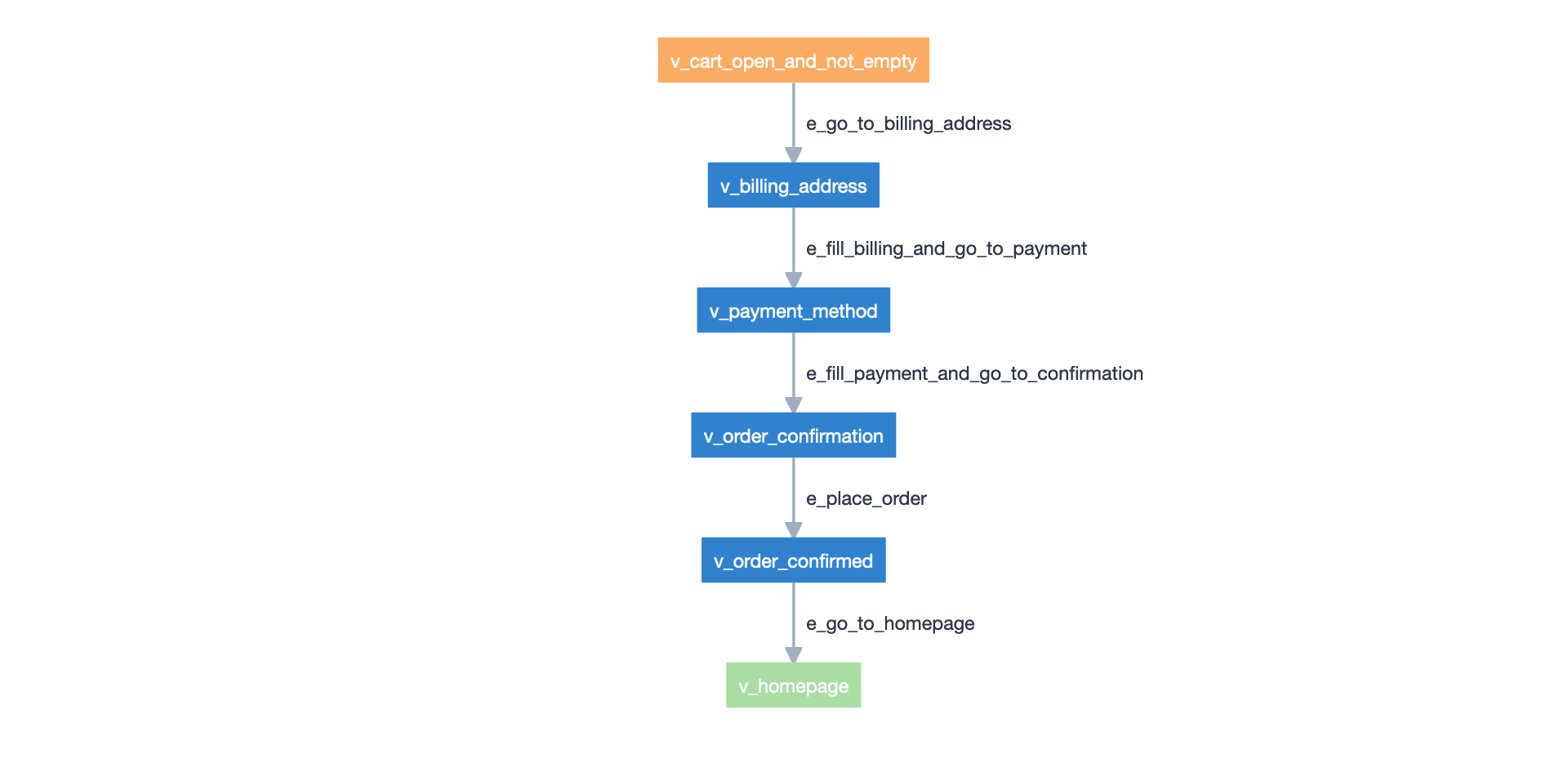
Screenshot of the CheckoutModel taken from the Model-Editor.#
Actions and Guards#
The global.itemsInCart variable is initialized at start in
NavigationModel’s actions:
{
"actions": [
"global.itemsInCart = 0;"
]
}
The actions from the model level will be executed before any element from the model.
And its value is updated in add_to_cart_from_homepage,
add_to_cart_from_product_page and e_place_order, where it’s
increased by one each time one of the three edges is reached:
{
"actions": [
"global.itemsInCart++;"
]
}
The cart_open_and_not_empty vertex from NavigationModel* has
4 edges linked into it. All of the 4 edges are guarded by:
{
"guard": "global.itemsInCart > 0"
}
That means that GraphWalker will not generate a path that goes
through the guarded edges unless global.itemsInCart is greater than 0.
This way we make sure that every time we reach cart_open_and_not_empty
we have items in cart and we can jump to CheckoutModel.
Tests#
The tests can be found inside tests package.
We use Selenium and PyPOM (Python Page Object Model) to interact with the
e-commerce website. The code that interacts with the page, is inside
tests/pages/ package.
Each model defined in models/default.json has an associated class in
tests/test.py. The models/default.json contains two models:
NavigationModel and CheckoutModel, so test/test.py contains two
classes named after each model: NavigationModel and CheckoutModel.
Each model class has a method for each edge and vertex from the corresponding model.
During execution of tests, whenever the path reaches the vertex with the id
v_homepage defined in the NavigationModel model, AltWalker will execute
the method: tests/test.py::NavigationModel::homepage.
Structure#
tests/
pages/
__init__.py
base.py
home.py
product.py
__init__.py
test.py
Inside tests/page/ we define our Page Object Model for the home and
product pages.
Inside tests/test.py we define our test code for our model(s).
Fixtures#
We use the setUpRun and tearDown fixtures to manage Selenium’s
WebDriver session.
Inside the setUpRun function we create the selenium driver:
def setUpRun():
# ...
print("Create a new Firefox session")
driver = webdriver.Firefox(options=options)
# ...
And in the tearDownRun we close the driver:
def tearDownRun():
# ...
print("Close the Firefox session")
driver.quit()
Further Reading/Useful Links#
PyPOM (Python Page Object Model)
Checking the Models#
$ altwalker check -m models/navigation.json "random(edge_coverage(100))"
Checks the integrity of the model(s).
You can also check multiple models this will also check that all models can be reached.
$ altwalker check -m models/navigation.json "random(edge_coverage(100))" -m models/checkout.json "random(vertex_coverage(100))"
Verifying the Code#
$ altwalker verify -m models/navigation.json tests
Verifies that your model and tests are valid, and that all names
referred in the model are implemented in tests package.
Running the Tests#
AltWalker provides two ways of running the tests:
- Online Mode (On the fly)
Generate one step at a time and execute it.
- Offline Mode
Generate a list of steps which can be executed later.
Online Mode#
$ altwalker online -m models/navigation.json "quick_random(edge_coverage(100))" tests
Walks randomly through the graph until all edges have been passed.
You can also run tests with two models.
$ altwalker online -m models/navigation.json "random(edge_coverage(100))" -m models/checkout.json "random(edge_coverage(100))" tests
Offline Mode#
$ altwalker offline -m models/navigation.json "random(length(15))" -f steps.json
Generates a valid path through the test graph and saves the list of
steps into steps.json.
Note
The offline command doesn’t run the tests it only generates a path.
$ altwalker walk tests ./steps.json
Executes (walks on) the steps from the steps.json file.