Overview#
AltWalker is an open source Model-Based Testing framework that supports running tests written in python3 and .NET/C#. You design your tests as a directed graph and AltWalker generates test cases from your graph (using GraphWalker) and executes them.
Model-Based Testing#
Model-Based Testing is a testing technique which offers a way of generating test cases based on models that describe the behavior (functionality) of the system under test.
The goal when designing models is to represent the part of the system under test, usually by one model for each functionality of your system.
With the help of graph theory we can dynamically generate multiple test scripts. A test script is a path passing through the model from a starting point till a condition is met.
Why use Model-Based Testing:
the abstraction layer added by the model gives your tests a better structure
the model can be updated to reflect the requirements changes making the tests easy to maintain
dynamically generates multiple test scripts based on different conditions (like coverage or length)
allows for a large number of tests to be created which results in a larger part of the system under test to be covered.
AltWalker#
AltWalker is a test execution tool, which aims to make it easy to write and run your model-based tests. It uses GraphWalker to generate a path through the models.
For the test structure it uses an Object-Oriented approach inspired by python’s unittest
module. Every model is mapped to a class with the same name and each vertex and edge from the
model is mapped to a method inside the class.
AltWalker also borrows the concept of test fixture from unit tests, and implements the following
fixtures: setUpRun, tearDownRun, setUpModel and tearDownModel.
Now it supports running tests written in .NET/C# and Python3.
AltWalker Components#
AltWalker has the following components:
Model: a directed graph, supplied by the user as a json or graphml file. A graph is composed from a list of vertices and a list of edges.
Generator and Stop Condition: used to specify how to generate a path and to decide when a path is complete.
Test Code: the implementation of the model(s) as code. Each model is mapped to a class and each vertex and edge is mapped to a method.
Planner: uses the model(s) and a pair of generator and stop condition to provide a path (a sequence of steps) through the model(s).
Currently AltWalker provides two planners:
Online Planner
Offline Planner
Reporter: reports the output of the tests, the reporter is called on each event (e.g.
step_start,step_end, …).Executor: for each step in the plan it looks up and calls the named method from the test code. In addition to the step methods, it also calls fixture methods if present (e.g.
setUpModel,tearDownModel…).Currently AltWalker provides three executors:
Python Executor (Built-in)
Http Executor that allows you to hook up your own executor via HTTP. You can read more about the Http Executor on the Write your own executor section.
Walker: the test runner. Coordinates the execution of a test asking the
Plannerfor the next step, executing the step using theExecutorand reporting the progress using theReporter.
There are two ways to run your tests:
Online Mode (using the Online Planner): Generate one step and then execute the step, until the path is complete.
Offline Mode (using the Offline Planner): Run a path from a sequence of steps. Usually the path is generated using the
offlinecommand.
GraphWalker#
GraphWalker is an Model-Based Testing tool. It reads models in the shape of directed graphs, and generates (test) paths from these graphs.
AltWalker uses GraphWalker as a Planner (it uses the REST API as the Online Planner), so it inherits the model(s) formats (graphml and json) and the generators and stop conditions.
AltWalker also uses the offline, check commands from GraphWalker.
The offline command form GraphWalker is used by the AltWalker’s offline command, it takes
the output and saves it in a file as a list of steps.
The check command from GraphWalker is used by AltWalker’s check.
Model Editor#
The Model Editor is a web-based tool that serves as both an editor and visualizer for models written in the GraphWalker JSON format.
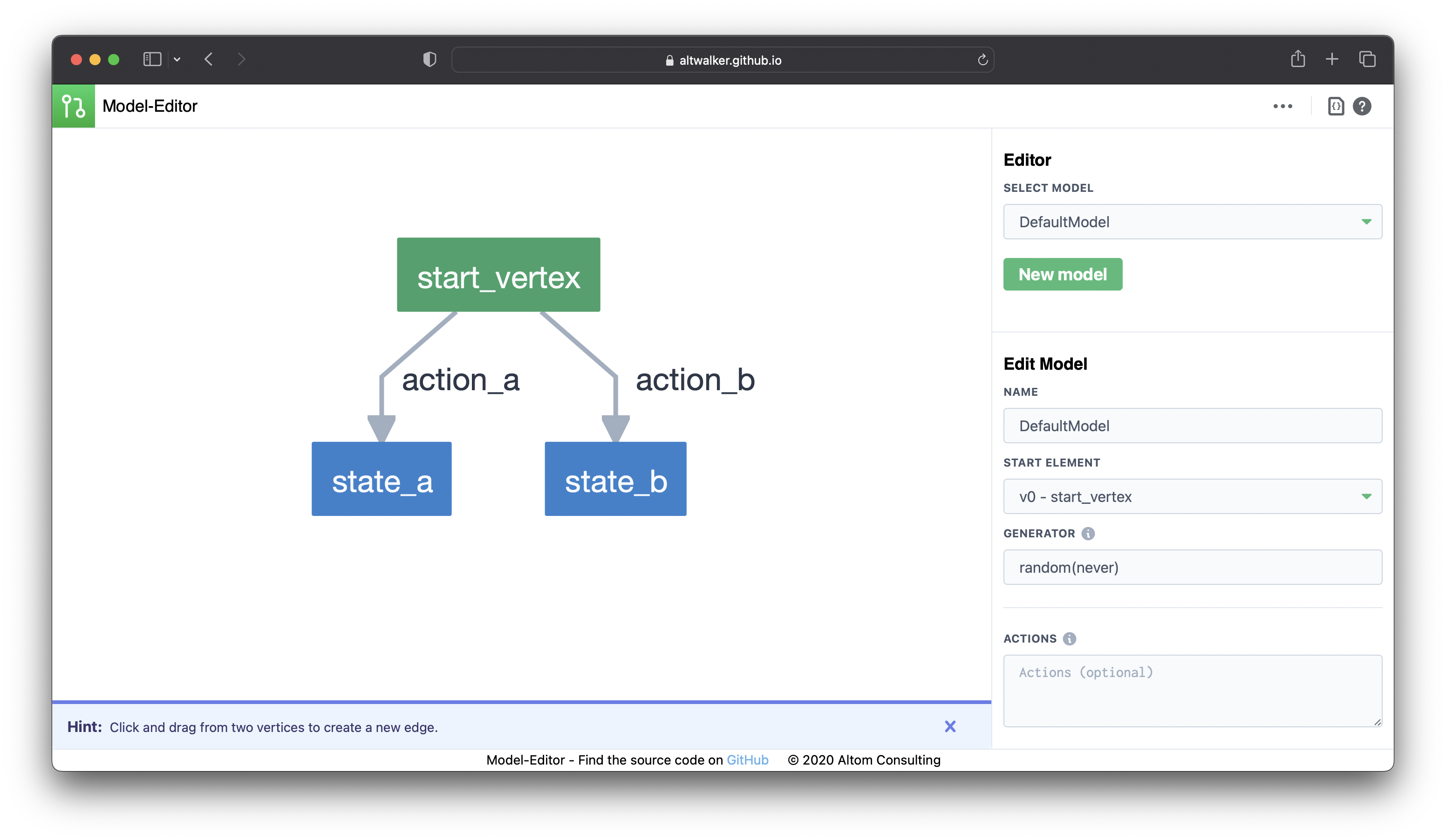
Screenshot taken from the Model Editor.#
VS Code Extension#
If you’re a VS Code user, you can explore the AltWalker’s Model Visualizer Extension, which enables you to visualize your model in real-time while you work on it.
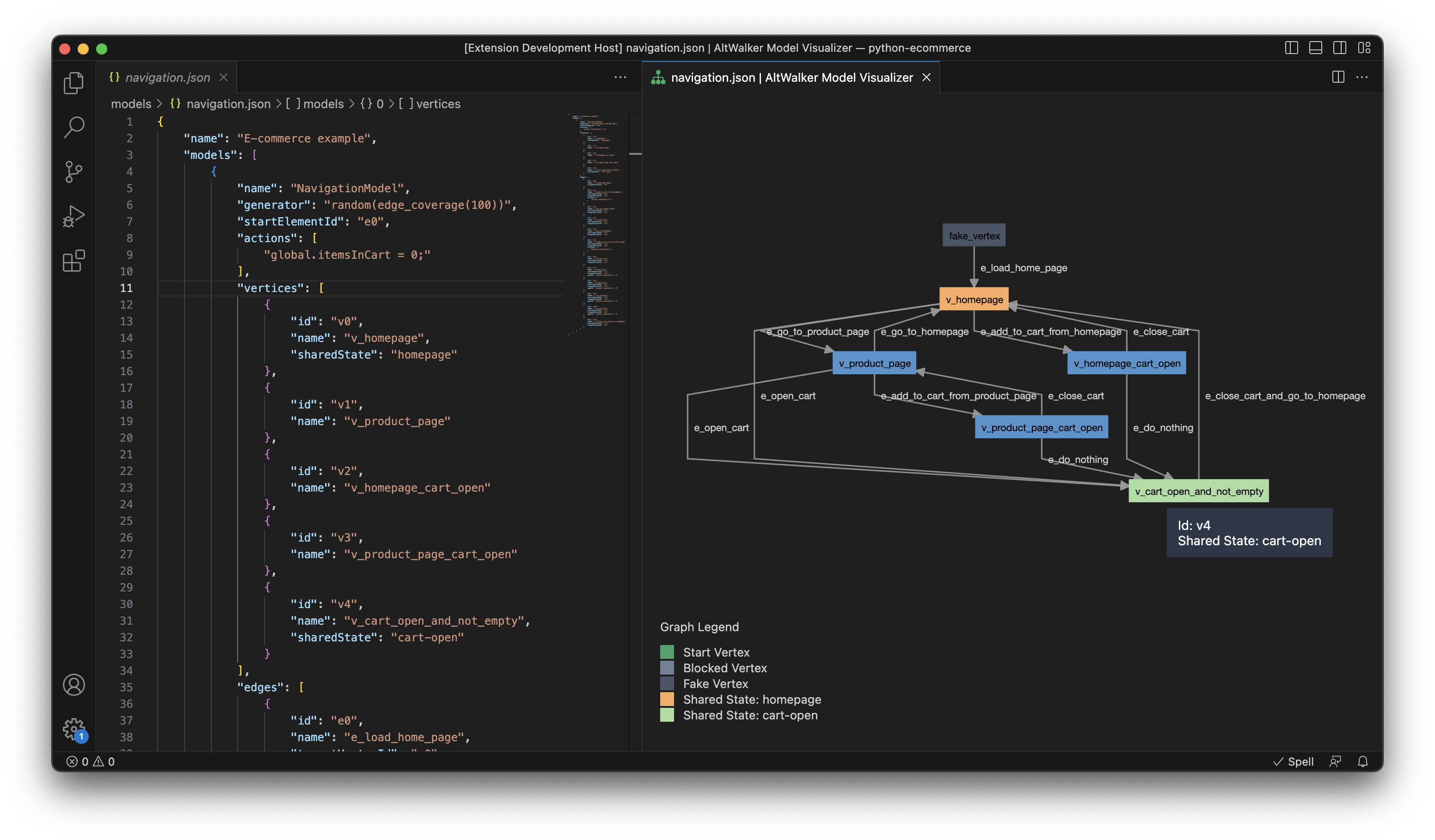
Screenshot taken from the AltWalker Model-Visualizer VS Code Extension.#
Live Viewer#
AltWalker’s Live Viewer is a powerful tool designed to enhance your experience with AltWalker. This application provides real-time visualization and monitoring capabilities for your AltWalker test runs, allowing you to gain deeper insights into test execution, track progress, and identify potential issues with ease. With AltWalker’s LiveViewer, you can effortlessly keep an eye on the execution of your test models and ensure the success of your testing endeavors.
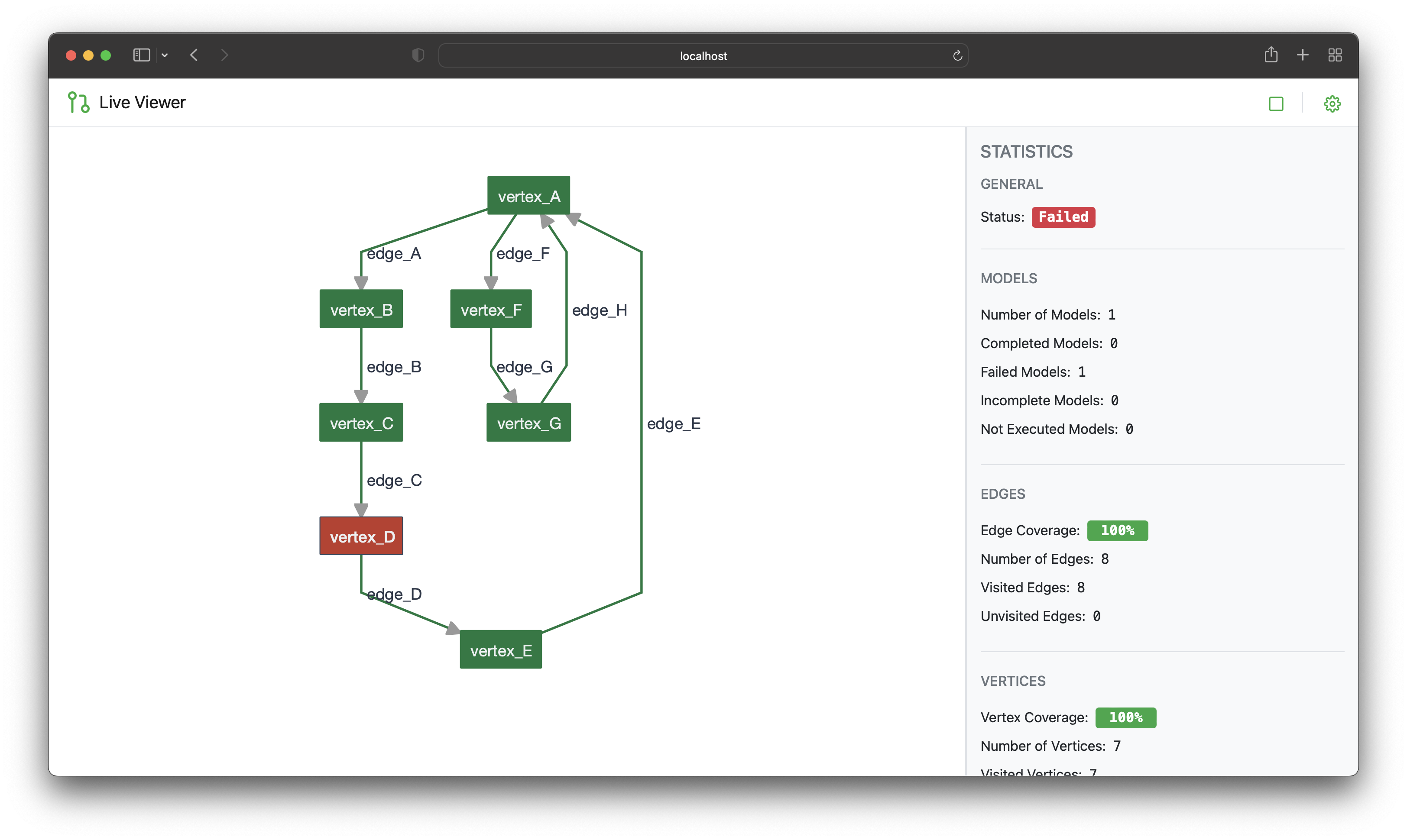
Screenshot taken from the AltWalker LiveViewer.#